
- Aws postgresql apache django how to#
- Aws postgresql apache django for mac#
- Aws postgresql apache django install#
- Aws postgresql apache django full#
- Aws postgresql apache django windows#
Aws postgresql apache django install#
Next we need to install the EB CLI, which will enable us to remotely interact with our Elastic Beanstalk environment. Installing the Elastic Beanstalk Command Line Interface Finally upload the aws-eb.pub file inside. Under “Name” type “aws-eb”, then click “Browse” and navigate to your. On the upper right hand side of the Key pairs screen click “Actions > Import key pair”. On the left-hand side under “Network & Security” select “Key Pairs”. Note that certain regions outside the US might not have various AWS components available yet, so I would advise using a region inside America when starting. If you are unsure of which region to work with, it’s usually a good idea to pick the one closest to you for performance purposes.

Open your AWS EC2 key console and in the upper right hand corner select the region in which you will be establishing your environment. Which will open up an Explorer window for the.
Aws postgresql apache django windows#
If you are on a Windows machine you can now type: ii. The second creates an ssh key named “aws-eb”. The first line changes our current directory to your user profile’s.
Aws postgresql apache django for mac#
Open Windows Powershell (or terminal for Mac users) and type the following (replacing with your email): cd ~/.ssh Down the road, this will prevent us from accessing our environment’s server directly via ssh, so it’s best to generate our keypair using our local shell. While users are able to create keys directly in the Amazon EC2 console, they will not be able to add a passphrase using this method. This will allow our machine to create a secure, encrypted connection to Amazon.
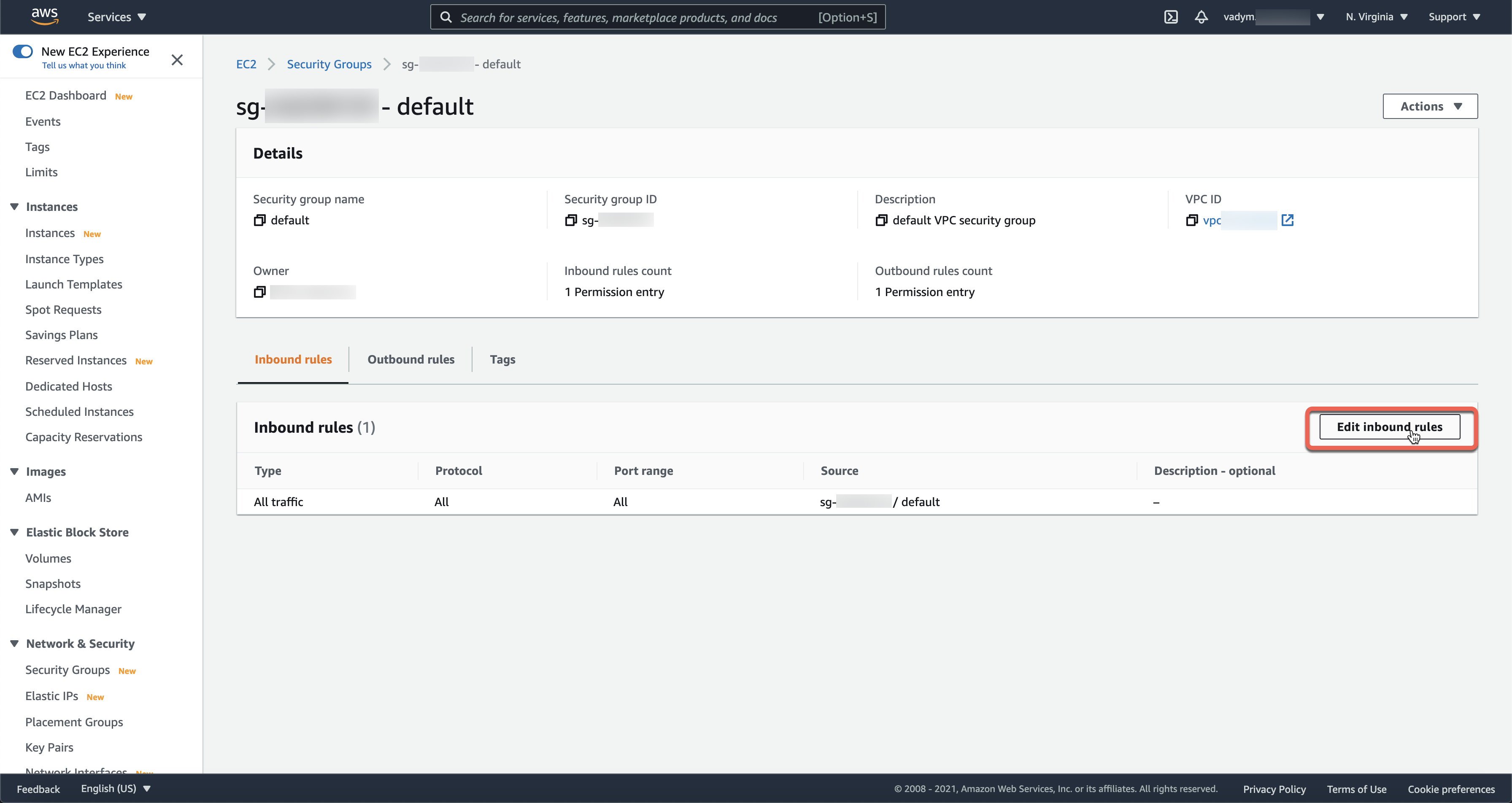
In order to use this tool effectively, we must setup a ssh key pair. EC2 Key Pair Setupīelow we will be using Elastic Beanstalk command line interface (EB CLI) to help setup our remote environment and execute various commands.

If no such account exists, click “Add user” and follow the setup instructions. Once there, make sure sure you have at least one entity with admin permissions available. Log into your AWS console with your root username and password, and under “Security, Identity, & Compliance” enter the Identity and Access Management panel by clicking “IAM”. To utilize any of Amazon Web Services, you’ll need at least one IAM account setup with elevated permissions. To avoid potential future headaches, I recommend sticking with the earlier release. While there is a newer Anaconda3-2020.07 distribution, the Python 3.8 version it runs creates difficulties while trying to interface with mod_wsgi and Apache on your local machine. I found this to be the most suitable option as of this writing, given that the latest Elastic Beanstalk environment runs Python 3.7.9. Local Python Environmentīecause work with a fair number of projects related to data science, I used Anaconda3-2019.10 (available through their archives) which runs Python 3.7.4. For a brief refresher on the structure of a Django project and some useful commands, you can refer to our quick start guide.
Aws postgresql apache django full#
If you are unfamiliar with the latter, I highly recommend watching the Python Django Web Framework – Full Course For Beginners which will give you 95% of the skills you need in just 4 hours. This post assumes you have a working knowledge of Python and Django.
Aws postgresql apache django how to#
More importantly, however, I hope he or she will understand how to update them as Amazon inevitably rolls out new environments with different structures. In this way I hope the reader will be able to adapt the settings to meet their specific needs. Accordingly, my goal is not just to provide the commands necessary to setup your web app, but break down what these commands do. While much of the process is streamlined via web GUIs, there are a few key components that require config files or platform hooks that may be intimidating for the newly initiated. With that in mind, below I attempt to describe how to deploy a Django app on Amazon’s Elastic Beanstalk framework using Amazon Linux 2, Postgresql, and Python 3.7. Throughout the proceeding setup I thought it was a tinge ironic how a platform touted as the easiest for startups and best for scaling was riddled with so many pitfalls for newcomers, and based on the comments I observed in countless different online forums, it seemed I was not alone. Given that Amazon had just rolled its new Linux 2 flavor, my timing on this could not have been better for educational purposes nor worse for my blood pressure. Having written a number of small Django applications on my local computer, I recent decided to try productionizing my first app using AWS.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
